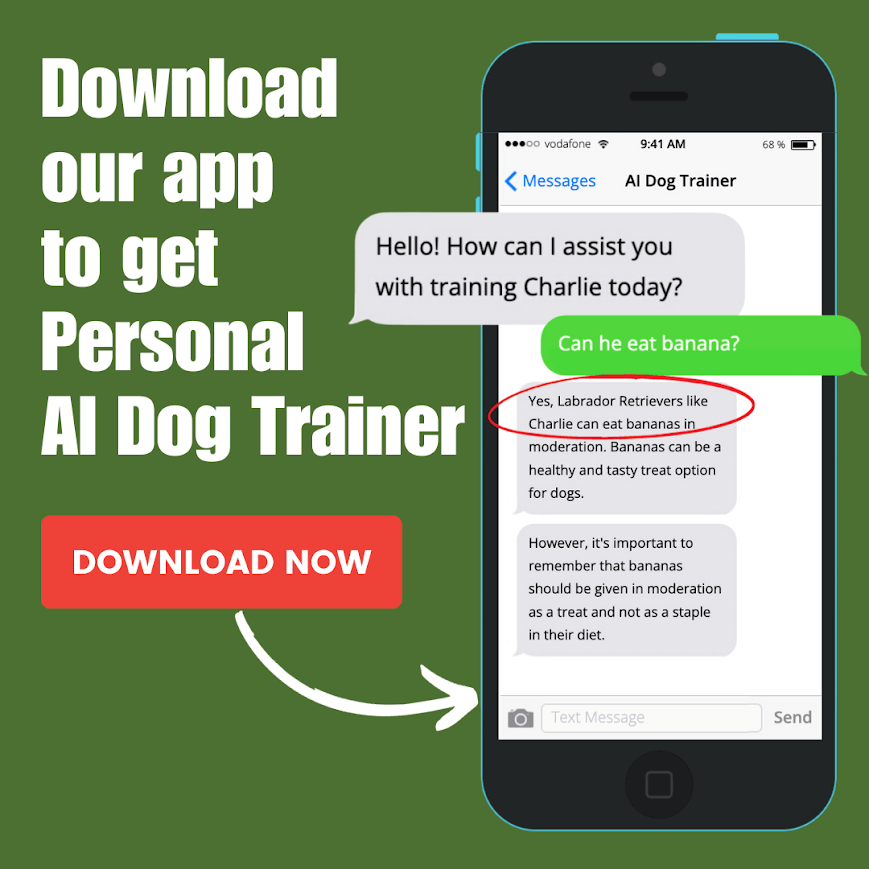
If you are a cat owner, you probably know how important it is to keep an eye on your cat’s health and well-being. One of the vital metrics that can help you assess your cat’s wellness is their respiration rate, or how fast they breathe per minute when they are resting, calm, or asleep.
In this article, we will explain what cat respiration rate is, why it is important to measure it, how to measure it, what does a decreased or elevated breathing rate mean, and how to prevent or treat breathing problems in cats.
What Is Cat Respiration Rate and Why Is it Important?
Cat respiration rate is the number of breaths a cat takes per minute when they are at rest or asleep. A breath is counted as one inhalation and one exhalation of air through the nose or mouth.
A normal respiration rate for a healthy cat is between 15 and 30 breaths per minute , but this can vary depending on several factors, such as age, breed, size, and health conditions.

Measuring your cat’s respiration rate can help you detect any signs of respiratory distress, heart problems, infections, anemia, or other issues that affect their oxygen and blood circulation.
Respiratory distress is a serious condition that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. It occurs when a cat has difficulty breathing or does not get enough oxygen in their blood. Some of the symptoms of respiratory distress include:
- Rapid breathing (more than 40 breaths per minute)
- Shallow breathing
- Labored breathing (using abdominal muscles or open mouth)
- Noisy breathing (wheezing, coughing, sneezing)
- Bluish or pale gums
- Lethargy
- Loss of appetite
- Restlessness
- Anxiety
If you notice any of these symptoms in your cat, you should contact your vet immediately and seek emergency care.
How to Measure Your Cat’s Breathing Rate
Measuring your cat’s breathing rate is easy and non-invasive. You don’t need any special tools or equipment, just a timer or a watch. Here are the steps to follow:
- Find a time when your cat is resting comfortably or sleeping, but not purring. Purring can affect your cat’s breathing rate and make it harder to count,
- Observe your cat’s chest movement or feel their heartbeat with your hand. Start your timer or watch and count how many breaths your cat takes in 30 seconds. One breath means one full inhale and one full exhale.
- Multiply the number of breaths by two to get the number of breaths per minute.
For example, if you count 10 breaths in 30 seconds, then your cat’s respiration rate is 10 x 2 = 20 breaths per minute.
You should measure your cat’s respiration rate several times to get an average and a baseline. You should also measure it at different times of the day and under different conditions to see how it varies.
You can keep a record of your cat’s respiration rate in a notebook or an app. This way, you can track any changes over time and share them with your vet if needed.
What Does a Decreased or Elevated Breathing Rate Mean?
A decreased or elevated breathing rate can indicate that your cat is experiencing some health issues that affect their respiratory system or their heart function. Some of the possible causes and symptoms of abnormal breathing rates are:
- Tachypnea: This is when your cat breathes faster than normal (more than 40 breaths per minute).
It can be caused by various factors, such as stress, pain, fever, heat stroke, dehydration, shock, anemia, lung disease, heart disease, asthma, allergies, pneumonia, bronchitis, pleural effusion (fluid in the chest cavity), diaphragmatic hernia (a hole in the diaphragm), pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs), pulmonary embolism (blood clot in the lungs), etc.
Some of the symptoms of tachypnea include panting, open mouth breathing, increased heart rate, restlessness, anxiety, weakness, etc.

- Bradypnea: This is when your cat breathes slower than normal (less than 15 breaths per minute).
It can be caused by various factors, such as sedation, anesthesia, hypothermia (low body temperature), hypothyroidism (low thyroid hormone), head trauma, brain tumor, stroke, etc.
Some of the symptoms of bradypnea include drowsiness, confusion, loss of consciousness, coma, etc.
If you notice that your cat has a decreased or elevated breathing rate, you should consult your vet as soon as possible and find out the underlying cause and the appropriate treatment.
How to Prevent or Treat Breathing Problems in Cats
Breathing problems in cats can be prevented or treated by following some simple tips, such as:
- Provide your cat with fresh water and a balanced diet to keep them hydrated and nourished.
- Avoid exposing your cat to extreme heat or cold, as this can cause heat stroke or hypothermia, which can affect their breathing.
- Keep your cat’s environment clean and allergen-free, as dust, pollen, mold, smoke, chemicals, etc. can trigger respiratory irritation or infection.

- Follow your vet’s recommendations for vaccination, deworming, flea and tick prevention, dental care, etc. to protect your cat from diseases or parasites that can affect their respiratory system or their heart function.
- Monitor your cat’s weight and activity level, as obesity or lack of exercise can increase the risk of heart disease or respiratory problems.
- Follow your vet’s instructions for medication or surgery if your cat has a diagnosed condition that requires treatment. Some of the common treatments for breathing problems in cats include antibiotics, steroids, bronchodilators, oxygen therapy, diuretics, etc.
FAQs
What is considered a normal respiration rate for a cat?
A normal respiration rate for a cat ranges from 20 to 30 breaths per minute. Keep in mind that certain factors like age, activity level, and environmental temperature can slightly influence the rate.
Can stress affect my cat’s respiration rate?
Yes, stress can affect a cat’s respiration rate. When a cat is anxious or scared, their breathing may become more rapid. If your cat is experiencing stress, try to identify and alleviate the cause to promote better respiratory health.
Are there any specific breeds prone to respiratory issues?
Certain cat breeds, such as Persians and Himalayans, are more prone to respiratory issues due to their facial structure, which may affect their airways. Regular monitoring of their respiration rate is especially important for these breeds.
Does my cat’s age affect their respiration rate?
Yes, a cat’s age can influence their respiration rate. Kittens and older cats may have slightly higher respiratory rates compared to adult cats. If you’re concerned about any significant changes, consult your vet.
Conclusion
Cat respiration rate is a vital metric for assessing cat wellness. It can help you detect any signs of respiratory distress, heart problems, infections, anemia, or other issues that affect their oxygen and blood circulation.
A normal respiration rate for a healthy cat is between 15 and 30 breaths per minute, but this can vary depending on several factors.
You should measure your cat’s breathing rate regularly and consult your vet if you notice any changes or abnormalities.

Charlene Pare is the founder of Cat Likes Best. She manages and strategizes the content published on this website. When she isn’t working, she enjoys exploring the city around with her Ameican Shorthair kitty–Moli. Being a technocrat and an avid cat lover, she also writes on pet tech products and some of the featured articles.